


The verbs used in learning objectives or learning outcomes should correspond to the level of thought at which the learners are expected to perform or function. The following lists of verbs are provided to help recognize the levels of thought and to help you write learning objectives that address the various levels of skill your learner should attain. By creating learning objectives using these verbs, you indicate explicitly what the learner must do in order to demonstrate learning.
This list is arranged according to Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning. Bloom’s Taxonomy classifies thinking according to six cognitive levels of complexity: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. The categories are ordered from simple to complex and from concrete to abstract. Each level becomes more challenging as you move higher.
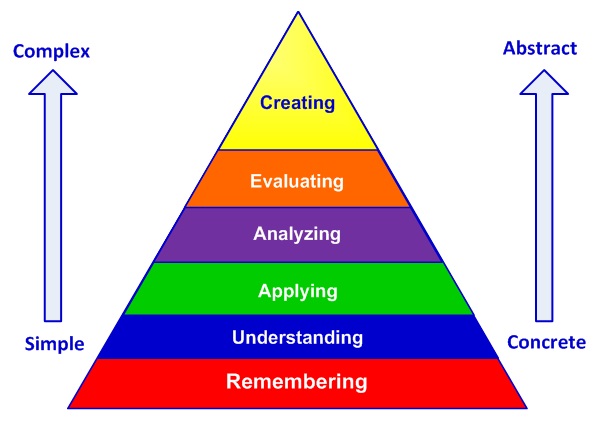
Cognitive competency or complexity begins at the knowledge level learning and advances up the taxonomy to comprehension, application, and then to the higher order thinking skills involved in analysis, synthesis, and evaluation.
When determining your learning objectives, consider using a verb from the appropriate cognitive domain below. This list will help you express specific performance expectations you have of the learners at the completion of the course.
This is the lowest level of learning. This cognitive level focuses on the ability to remember or retrieve previously learned material. The learning standards at this level simply ask the learner to recognize and recall data or information.
Examples of verbs that relate to the Knowledge domain are: